

Understanding Triggers in MCAS
For people living with MCAS, everyday life can sometimes feel like navigating a minefield of potential reactions. One of the key challenges of MCAS is that mast cells can become overly sensitive and react to a wide range of triggers, many of which are harmless for other people. These triggers can cause a sudden release of chemicals like histamine, leading to symptoms that affect multiple systems in the body.
Everyone’s experience with MCAS is different. While some people may have clear, consistent triggers, others may struggle with reactions that seem unpredictable or vary day to day. That’s why identifying and understanding your own triggers can be an important part of managing the condition.
Learning about common triggers and how they affect you personally can help reduce symptoms, prevent flares, and give you more confidence in daily life.

Understanding YOUR triggers
People with MCAS can react to a wide variety of triggers, and these triggers differ from person to person.
Triggers are anything that can cause mast cells to become activated and release chemical mediators like histamine, leading to symptoms.
Sometimes just one trigger is enough to cause a reaction; other times, it’s the combined effect of several small triggers that pushes the body over its threshold.
Each person’s trigger profile is unique, and it can take time to figure out what affects you. Even common triggers don’t impact everyone.
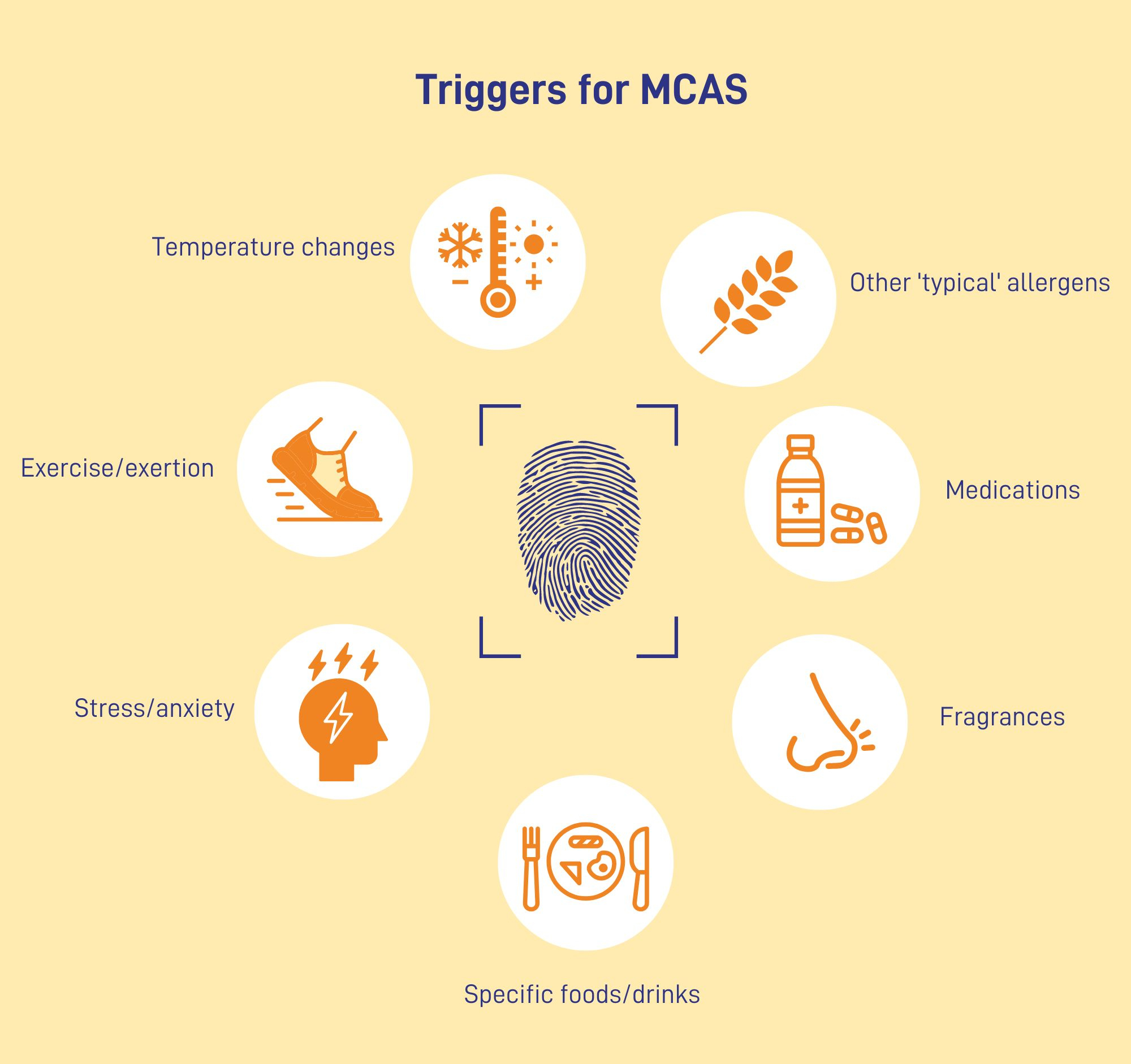
What Triggers MCAS Symptoms?
What sets off symptoms one day might be tolerated another, depending on factors like stress, illness, or cumulative exposure.
Common categories of triggers include certain foods, environmental factors like fragrances or temperature changes, medications or supplements, emotional or physical stress, infections, hormonal shifts, and even things like exercise or pressure on the skin.
Some people are triggered by just a few specific things, while others may feel reactive to many aspects of daily life.
Understanding your personal triggers takes time, but it can make a real difference in reducing flares and improving quality of life.

Specialist diets
Many people affected by MCAS find that foods are common triggers. Although sometimes it is obvious which food is triggering symptoms, this isn't always the case. Where we suspect food is the culprit, it can be difficult to identify food triggers as we usually consume multiple foods at the same time. Reactions are not always instant and can sometimes take several days to trigger symptoms. Therefore, a systematic approach is needed to reveal which foods or food groups are causing symtoms.
Some specialist diets can be helpful. Dietary management strategies most frequently used by people with MCAS are:
- Low histamine
- Dairy free
- Gluten free
- Low Salicylates
- Low oxalates
- Low FODMAP
- Low sugar (Ketogenic)
Or a combination of any of the above.
Elimination diets should only be implemented under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The food group should be removed for a period of 6 weeks and then foods reintroduced one by one to see if there is a reaction to an individual food.
A Healthcare professional must be involved with any restriction diets for children.
Become a friend
Sign up to become a Friend of Mast Cell Action so we can keep you up to date on our progress and on how to get involved in our latest campaigns and initiatives.
Donate
Mast Cell Action relies entirely on the generosity of people like you. Please make a donation now and together we can make a difference to those affected by MCAS.







